Regio- and Stereoselective C(sp2)-H Acylation of Enamides with AldehydesviaTransition-Metal Free Photoredox Catalysis
Kai Zhao,*aXiao-Chen Zhang,aJi-Yu Tao,aXian-Dan Wu,aJia-Xu Wu,aWei-Ming Li,aTong-Hao Zhu,*band Teck-Peng Loh*a, c
aInstitute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing 211816, China.
bInstitute of Advanced Studies, Taizhou University, 1139 Shifu Avenue, Taizhou 318000, China.
cDivision of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371, Singapore.
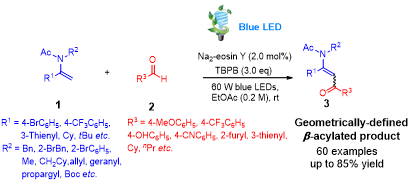
Abstract:A straightforward and efficient C(sp2)–H acylation of enamides with aldehydes via transition-metal free photoredox catalysis is demonstrated. The transformation proceeded smoothly without resorting to expensive and potentially toxic iridium or ruthenium polypyridyl based photocatalysts under mild conditions, furnishing a diverse range of synthetically crucial geometrically-definedβ-acylated enamides in a stereoselective and regioselective manner.
Green Chemistry.2020,22,5497-5503. (2019年影响因子:9.480).
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1039/D0GC01947J
