报告时间:2016年8月15日上午9:30
报告地点:科技创新大楼C501室
报告题目:Applications of Conjugated Polyelectrolytes in Biosensing and Disinfection
Applications of Conjugated Polyelectrolytes in Biosensing and Disinfection
Kirk S. Schanze
Department of Chemistry and Center for Macromolecular Science and Engineering,
University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA 32611-7200
E-mail:kschanze@chem.ufl.edu
Conjugated polyelectrolytes (CPEs) featuring poly(phenylene ethynylene) and poly(thiophene) backbones substituted with ionic solubilizing groups are water soluble. These materials display a variety of interesting properties, including self-assembly into nanoscale aggregates, ability to process into layer-by-layer films and optical/stimuli responsive behaviour in the presence of ions, surfactants and biomacromolecules. We have explored the use of cationic CPEs as fluorescent sensors for polyphosphates (pyrophosphate, ATP and ADP). In addition, cationic CPEs exhibit strong light-activated biocidal activity vs. a broad spectrum of bioagents, including bacteria, virus particles and spores. The talk will overview recent work in this area, including the interaction with cationic CPEs with mammalian cells.
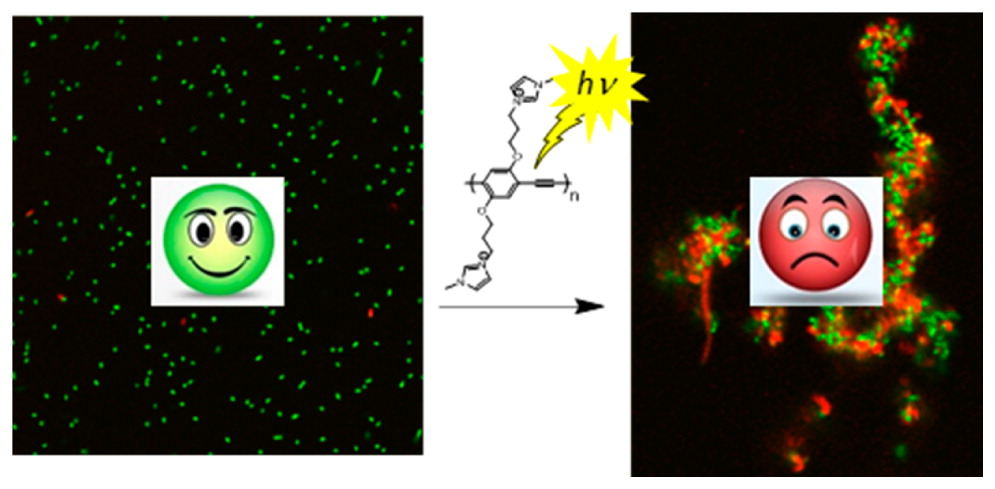
[1] Jiang, H.; Taranekar, P.; Reynolds, J. R.; Schanze, K. S. “Conjugated Polyelectrolytes: Synthesis, Photophysics, and Applications”, Angew. Chem. 2009, 48, 4300-4316, DOI: 10.1002/anie.200805456.
[2] Wu, D.; Schanze, K. S. “Protein Induced Aggregation of Conjugated Polyelectrolytes Probed with Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy: Application to Protein Identification”, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7643-7651, DOI: 10.1021/am5009437.
[3] Parthasarathy, A.; Pappas, E. H.; Hill, E. H.; Huang, Y.; Whitten, D. G.; Schanze, K. S. “Conjugated Polyelectrolytes with Imidazolium Solubilizing Groups. Properties and Application to Photodynamic Inactivation of Bacteria”, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28027-28034, DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02771.
