探索具有印刻快速响应的新型传感材料是先进材料的研究热点之一。重点实验室陈苏教授、博士生杨胜洋及其王彩风博士在国家自然科学基金(Grant 10976012, Grants 21076103 及Grants 21006046)和材料化学工程国家重点实验室基金的支持下,在释放诱导响应聚合物纳米纤维膜传感材料领域取得重要进展,其研究成果日前刊登在国际化学领域顶级刊物德国《应用化学》上(影响因子11.829,2009)(“A Release-Induced Response for Rapid Recognition of Latent Fingermarks and Formation of Inkjet-Printed Patterns”,Angrewandte Chemie International Edition, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201006537)。
这项研究提出了一种制备新型面向指纹识别、印刻快速响应的聚合物纳米纤维膜传感材料的新方法。该方法新颖、易于操控,其传感材料可快速响应,价廉性能优越,且成功地在具有微纳结构的聚合物纤维膜印刻了代表中国龙的吉祥图案。受到评阅人高度评价。认为该论文创新设计出一种新型灵巧聚合物纳米纤维膜传感材料,无论是技术上还是方法上都具有很好的创新性。该成果标志着材料化学工程国家重点实验室在聚合物纳米纤维传感材料方面已达到了一个新的高度。
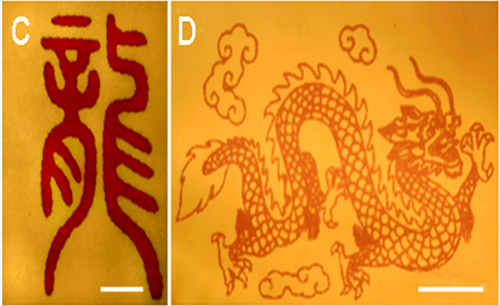
Enter the dragon: An electrospun nanofiber mat is used to identify latent fingerprints on various surfaces within 30 seconds and produce inkjet-printed patterns. In contrast to classical approaches, the method is easy-to-operate, environmentally friendly, and has implications in other applied systems including chemical sensors, drug delivery, biological detection, and microreactors.
